Connect to the Contract
Up to this point, we have prepared the UI for the frontend and successfully connected to the wallet!
In this lesson, you will deploy your smart contract and connect it to the frontend.
🌵 Let’s Implement the Connection to the Contract
We will continue working with files inside the packages/client directory.
📁 hooks Directory
Inside the hooks directory, create a file named useContract.ts and write the following code in it.
💁 At this stage, there are imports from files that we have not yet created, so it’s okay if you see error messages for now.
import { BigNumber, ethers } from "ethers";
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { USDCToken as UsdcContractType } from "../typechain-types";
import { JOEToken as JoeContractType } from "../typechain-types";
import { AMM as AmmContractType } from "../typechain-types";
import AmmArtifact from "../utils/AMM.json";
import { getEthereum } from "../utils/ethereum";
import UsdcArtifact from "../utils/USDCToken.json";
import JoeArtifact from "../utils/USDCToken.json";
export const UsdcAddress = "Contract deployment address";
export const JoeAddress = "Contract deployment address";
export const AmmAddress = "Contract deployment address";
export type TokenType = {
symbol: string;
contract: UsdcContractType | JoeContractType;
};
export type AmmType = {
sharePrecision: BigNumber;
contract: AmmContractType;
};
type ReturnUseContract = {
usdc: TokenType | undefined;
joe: TokenType | undefined;
amm: AmmType | undefined;
};
export const useContract = (
currentAccount: string | undefined
): ReturnUseContract => {
const [usdc, setUsdc] = useState<TokenType>();
const [joe, setJoe] = useState<TokenType>();
const [amm, setAmm] = useState<AmmType>();
const ethereum = getEthereum();
const getContract = useCallback(
(
contractAddress: string,
abi: ethers.ContractInterface,
storeContract: (_: ethers.Contract) => void
) => {
if (!ethereum) {
console.log("Ethereum object doesn't exist!");
return;
}
if (!currentAccount) {
// Since calling a contract function without being logged in will fail,
// if currentAccount is undefined, the contract object is also set to undefined.
console.log("currentAccount doesn't exist!");
return;
}
try {
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(
ethereum as unknown as ethers.providers.ExternalProvider
);
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // For simplicity, no argument is provided = use the first account (account #0).
const Contract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, abi, signer);
storeContract(Contract);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
[ethereum, currentAccount]
);
const generateUsdc = async (contract: UsdcContractType) => {
try {
const symbol = await contract.symbol();
setUsdc({ symbol: symbol, contract: contract } as TokenType);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
const generateJoe = async (contract: UsdcContractType) => {
try {
const symbol = await contract.symbol();
setJoe({ symbol: symbol, contract: contract } as TokenType);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
const generateAmm = async (contract: AmmContractType) => {
try {
const precision = await contract.PRECISION();
setAmm({ sharePrecision: precision, contract: contract } as AmmType);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
useEffect(() => {
getContract(UsdcAddress, UsdcArtifact.abi, (Contract: ethers.Contract) => {
generateUsdc(Contract as UsdcContractType);
});
getContract(JoeAddress, JoeArtifact.abi, (Contract: ethers.Contract) => {
generateJoe(Contract as JoeContractType);
});
getContract(AmmAddress, AmmArtifact.abi, (Contract: ethers.Contract) => {
generateAmm(Contract as AmmContractType);
});
}, [ethereum, currentAccount, getContract]);
return {
usdc,
joe,
amm,
};
};
At the top of the file, we are importing the necessary functions and defining types. 💁 Since there are imports from files that have not yet been created at this stage, you may see error messages — you can safely ignore them for now.
export type TokenType = {
symbol: string;
contract: UsdcContractType | JoeContractType;
};
This is for the token contract object that will be used in the frontend.
It stores an instance and the token symbol of either the USDC or JOE contract as a string.
export type AmmType = {
sharePrecision: BigNumber;
contract: AmmContractType;
};
This is the type definition for the AMM contract object that will be used in the frontend.
It stores the AMM contract instance along with the PRECISION value.
const getContract = useCallback(
(
contractAddress: string,
abi: ethers.ContractInterface,
storeContract: (_: ethers.Contract) => void
) => {
if (!ethereum) {
console.log("Ethereum object doesn't exist!");
return;
}
if (!currentAccount) {
// Since calling a contract function without being logged in will fail,
// set the contract object to undefined if currentAccount is undefined.
console.log("currentAccount doesn't exist!");
return;
}
try {
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(
ethereum as unknown as ethers.providers.ExternalProvider
);
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // For simplicity, no argument is provided = use the first account (account #0).
const Contract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, abi, signer);
storeContract(Contract);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
[ethereum, currentAccount]
);
getContract is a function that retrieves a contract instance using the address and ABI specified in its arguments.
Once the instance is obtained, it is passed to the function provided as an argument.
storeContract(Contract);
const generateUsdc = async (contract: UsdcContractType) => {
try {
const symbol = await contract.symbol();
setUsdc({ symbol: symbol, contract: contract } as TokenType);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
const generateJoe = async (contract: UsdcContractType) => {
try {
const symbol = await contract.symbol();
setJoe({ symbol: symbol, contract: contract } as TokenType);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
const generateAmm = async (contract: AmmContractType) => {
try {
const precision = await contract.PRECISION();
setAmm({ sharePrecision: precision, contract: contract } as AmmType);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
Each contract instance passed as an argument is converted into an object to be used in the frontend.
useEffect(() => {
getContract(UsdcAddress, UsdcArtifact.abi, (Contract: ethers.Contract) => {
generateUsdc(Contract as UsdcContractType);
});
getContract(JoeAddress, JoeArtifact.abi, (Contract: ethers.Contract) => {
generateJoe(Contract as JoeContractType);
});
getContract(AmmAddress, AmmArtifact.abi, (Contract: ethers.Contract) => {
generateAmm(Contract as AmmContractType);
});
}, [ethereum, currentAccount, getContract]);
From retrieving each contract to creating the corresponding object.
💥 Let’s deploy the contract to the testnet
Now that we’ve created the connection part for the contract, we’ll deploy it to the testnet so it can be used.
Navigate to the packages/contract directory.
Create a file named .env and enter the following:
Replace "YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY" with the private key of your account.
TEST_ACCOUNT_PRIVATE_KEY="YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY"
Retrieving
YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY
- In your browser, click the MetaMask extension and switch the network to
Avalanche FUJI C-Chain.
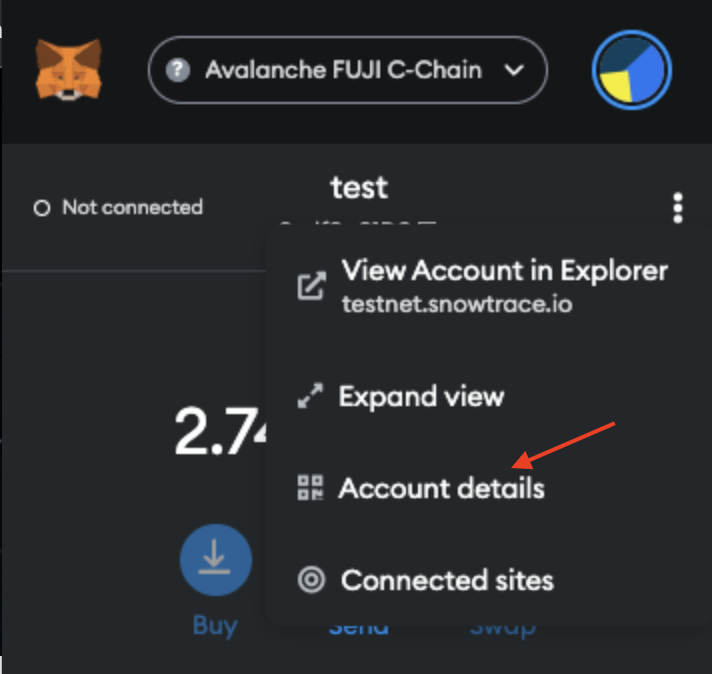
- Then select
Account details.
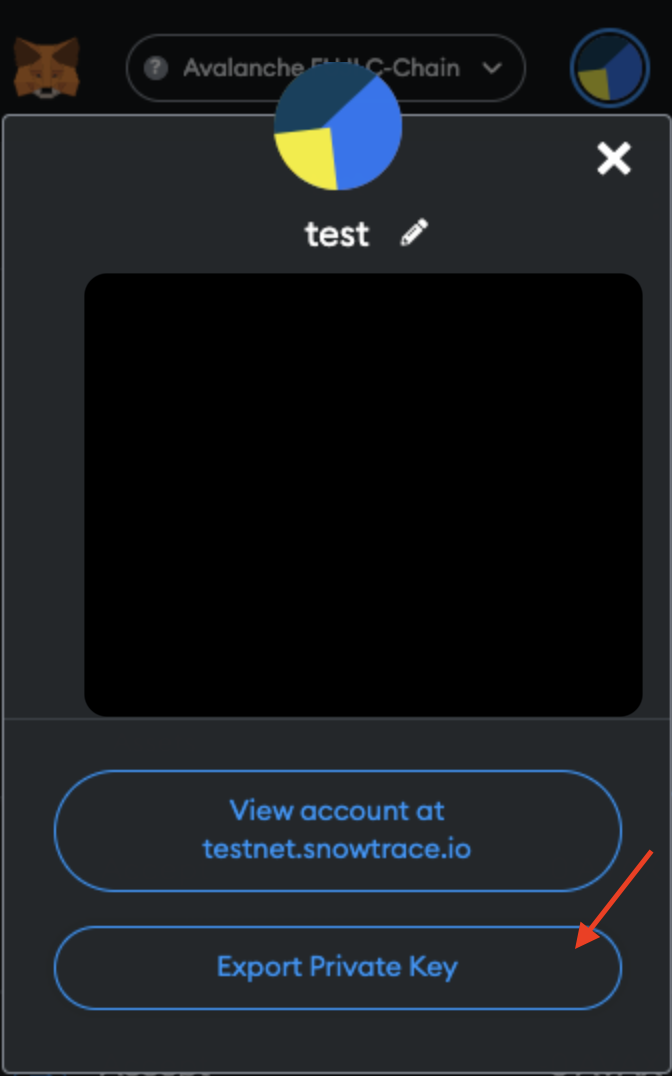
- In
Account details, clickExport Private Key.
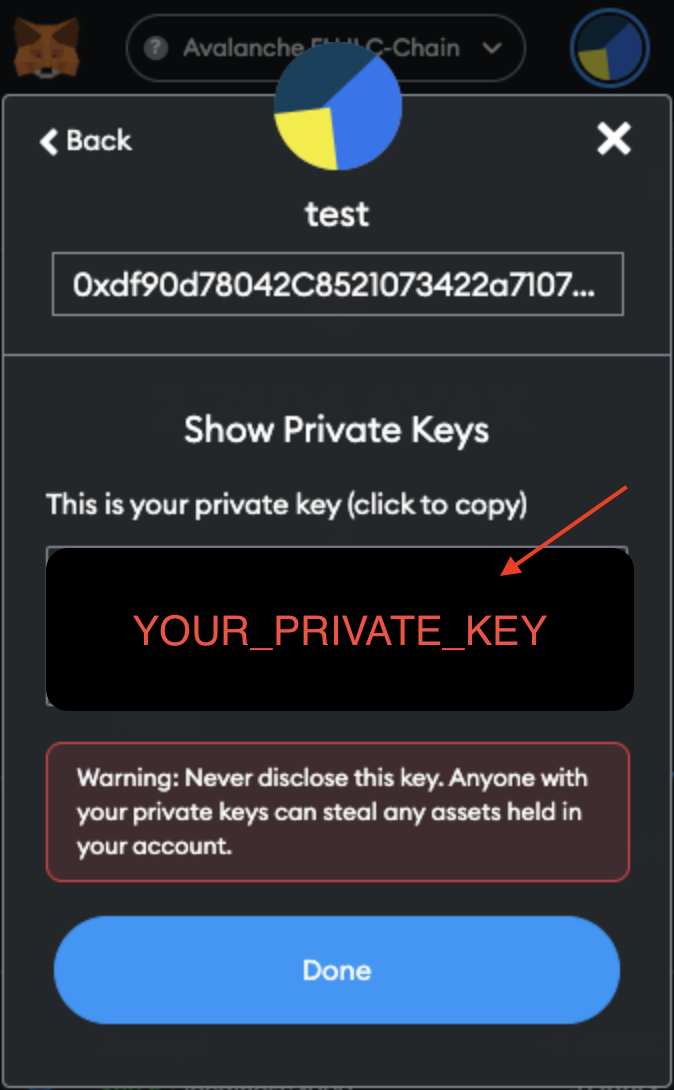
- You’ll be asked for your MetaMask password. Enter it and click
Confirm. Your private key (=Private Key) will be displayed—click to copy it.
- Replace the
YOUR_PRIVATE_KEYin.envwith the private key you just obtained.
⚠️ Make sure .env is listed in your gitignore file. Do not upload your private key to GitHub to prevent leakage.
✍️: Why a private key is required to deploy a smart contract > Deploying a new smart contract to the blockchain is also a kind of transaction.
To perform a transaction, you need to “log in” to the blockchain.
“Logging in” requires your public address and private key.
Next, overwrite the contents of hardhat.config.ts located directly under the packages/contract directory with the following code.
※ For the Solidity version (solidity: '0.8.17',), use the one that was originally specified.
import * as dotenv from "dotenv"; // This package was installed during the environment setup.
import "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox";
import { HardhatUserConfig } from "hardhat/config";
// Load environment variables from the .env file.
dotenv.config();
if (process.env.TEST_ACCOUNT_PRIVATE_KEY === undefined) {
console.log("private key is missing");
}
const config: HardhatUserConfig = {
solidity: "0.8.17",
networks: {
fuji: {
url: "https://api.avax-test.network/ext/bc/C/rpc",
chainId: 43113,
accounts:
process.env.TEST_ACCOUNT_PRIVATE_KEY !== undefined
? [process.env.TEST_ACCOUNT_PRIVATE_KEY]
: [],
},
},
};
export default config;
Next, overwrite deploy.ts inside the scripts directory with the following code.
import { ethers } from "hardhat";
async function deploy() {
// Get the address of the account that will deploy the contract.
const [deployer] = await ethers.getSigners();
// Deploy the USDC token contract.
const USDCToken = await ethers.getContractFactory("USDCToken");
const usdc = await USDCToken.deploy();
await usdc.deployed();
// Deploy the JOE token contract.
const JOEToken = await ethers.getContractFactory("JOEToken");
const joe = await JOEToken.deploy();
await joe.deployed();
// Deploy the AMM contract.
const AMM = await ethers.getContractFactory("AMM");
const amm = await AMM.deploy(usdc.address, joe.address);
await amm.deployed();
console.log("usdc address:", usdc.address);
console.log("joe address:", joe.address);
console.log("amm address:", amm.address);
console.log("account address that deploy contract:", deployer.address);
}
deploy()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
process.exit(1);
});
The contents of the deploy function are doing essentially the same thing as the deployContract function inside test/AMM.ts.
When you run this script while specifying the network you set earlier in hardhat.config.ts, the first account returned by ethers.getSigners() will be your account’s address.
In your terminal, make sure you are in the root directory of AVAX-AMM/, then run the following:
yarn contract deploy
If you see output like this, the deployment is successful! 🥳
yarn run v1.22.19
$ yarn workspace contract deploy
$ npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.ts --network fuji
usdc address: 0x5aC2B0744ACD8567c1c33c5c8644C43147645770
joe address: 0x538589242114BCBcD0f12B1990865E57b3344448
amm address: 0x1d09929346a768Ec6919bf89dae36B27D7e39321
account address that deploy contract: 0xdf90d78042C8521073422a7107262D61243a21D0
The addresses shown in the log are where each contract was deployed.
Save them somewhere safe — you’ll need them in the next step.
Finally, make sure that .gitignore includes .env!
🌵 Make smart contract information available to the frontend
Now that the contract is deployed, we’ll pass the smart contract information to the frontend so it can actually use it.
📽️ Copy the contract addresses
Take the three addresses displayed during contract deployment:
usdc address: 0x5aC2B0744ACD8567c1c33c5c8644C43147645770
joe address: 0x538589242114BCBcD0f12B1990865E57b3344448
amm address: 0x1d09929346a768Ec6919bf89dae36B27D7e39321
…and
paste them into the corresponding sections inside packages/client/hooks/useContract.ts.
export const UsdcAddress = "Contract deployment address";
export const JoeAddress = "Contract deployment address";
export const AmmAddress = "Contract deployment address";
例:
export const UsdcAddress = "0x5aC2B0744ACD8567c1c33c5c8644C43147645770";
export const JoeAddress = "0x538589242114BCBcD0f12B1990865E57b3344448";
export const AmmAddress = "0x1d09929346a768Ec6919bf89dae36B27D7e39321";
📽️ Get the ABI file
The ABI file is generated when the contract is compiled and is automatically stored in the artifacts directory.
From packages/contract, follow the path and you should find files for each contract in the format:
packages/contract/artifacts/contracts/~.sol/~.json
Copy these files into the utils directory inside client.
If you’re running the copy from the terminal at the root of AVAX-AMM, the command would look like this:
yarn contract cp:artifacts
📽️ Get the type definition file
Since TypeScript is a statically typed language, there are times when you want to know the type information of an object obtained externally. In such cases, type definition files come in handy.
The contract’s type definition files are generated when the contract is compiled and are automatically stored in the typechain-types directory.
This is because you selected TypeScript when running npx hardhat init, so the initial setup has already been done.
Copy the typechain-types directory inside contract directly into client.
If you’re running the copy from the terminal at the root of AVAX-AMM, the command would look like this:
yarn contract cp:typechain
With this, the contract information has now been successfully reflected.
Since we’ve prepared all the necessary files, the errors in the import statements at the top of client/hooks/useContract.ts should now be gone.
🌴 Let’s call contract functions
Now that the frontend is ready to use the contract, let’s actually try calling some functions.
Move into the client directory.
📁 components directory
📁 Details directory
Inside the components directory, create a new directory called Details.
Within it, create two files named Details.module.css and Details.tsx.
In Details.module.css, write the following code:
.details {
padding: 15px 10px 15px 0px;
width: 370px;
height: fit-content;
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.detailsBody {
background-color: #0e0e10;
width: 90%;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 19px;
}
.detailsHeader {
height: 30px;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: 600;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
color: white;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.detailsRow {
padding: 0px 25px;
height: 35px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.detailsAttribute {
font: 18px;
font-weight: 600;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-start;
width: 50%;
}
.detailsValue {
font: 18px;
font-weight: 900;
color: white;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
width: 50%;
}
This will be the CSS used in Details.tsx.
In Details.tsx, write the following code:
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import { useCallback, useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { AmmType, TokenType } from '../../hooks/useContract';
import { formatWithoutPrecision } from '../../utils/format';
import styles from './Details.module.css';
type Props = {
token0: TokenType | undefined;
token1: TokenType | undefined;
amm: AmmType | undefined;
currentAccount: string | undefined;
updateDetailsFlag: number;
};
export default function Details({
token0,
token1,
amm,
currentAccount,
updateDetailsFlag,
}: Props) {
const [amountOfUserTokens, setAmountOfUserTokens] = useState<string[]>([]);
const [amountOfPoolTokens, setAmountOfPoolTokens] = useState<string[]>([]);
const [tokens, setTokens] = useState<TokenType[]>([]);
const [userShare, setUserShare] = useState('');
const [totalShare, setTotalShare] = useState('');
const DISPLAY_CHAR_LIMIT = 7;
useEffect(() => {
if (!token0 || !token1) return;
setTokens([token0, token1]);
}, [token0, token1]);
const getAmountOfUserTokens = useCallback(async () => {
if (!currentAccount) return;
try {
setAmountOfUserTokens([]);
for (let index = 0; index < tokens.length; index++) {
const amountInWei = await tokens[index].contract.balanceOf(
currentAccount
);
const amountInEther = ethers.utils.formatEther(amountInWei);
setAmountOfUserTokens((prevState) => [...prevState, amountInEther]);
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}, [currentAccount, tokens]);
const getAmountOfPoolTokens = useCallback(async () => {
if (!amm) return;
try {
setAmountOfPoolTokens([]);
for (let index = 0; index < tokens.length; index++) {
const amountInWei = await amm.contract.totalAmount(
tokens[index].contract.address
);
const amountInEther = ethers.utils.formatEther(amountInWei);
setAmountOfPoolTokens((prevState) => [...prevState, amountInEther]);
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}, [amm, tokens]);
const getShare = useCallback(async () => {
if (!amm || !currentAccount) return;
try {
let share = await amm.contract.share(currentAccount);
let shareWithoutPrecision = formatWithoutPrecision(
share,
amm.sharePrecision
);
setUserShare(shareWithoutPrecision);
share = await amm.contract.totalShare();
shareWithoutPrecision = formatWithoutPrecision(share, amm.sharePrecision);
setTotalShare(shareWithoutPrecision);
} catch (err) {
console.log('Couldn't Fetch details', err);
}
}, [amm, currentAccount]);
useEffect(() => {
getAmountOfUserTokens();
}, [getAmountOfUserTokens, updateDetailsFlag]);
useEffect(() => {
getAmountOfPoolTokens();
}, [getAmountOfPoolTokens, updateDetailsFlag]);
useEffect(() => {
getShare();
}, [getShare, updateDetailsFlag]);
return (
<div className={styles.details}>
<div className={styles.detailsBody}>
<div className={styles.detailsHeader}>Your Details</div>
{amountOfUserTokens.map((amount, index) => {
return (
<div key={index} className={styles.detailsRow}>
<div className={styles.detailsAttribute}>
{tokens[index] === undefined
? 'loading...'
: tokens[index].symbol}
:
</div>
<div className={styles.detailsValue}>
{amount.substring(0, DISPLAY_CHAR_LIMIT)}
</div>
</div>
);
})}
<div className={styles.detailsRow}>
<div className={styles.detailsAttribute}>Share:</div>
<div className={styles.detailsValue}>
{userShare.substring(0, DISPLAY_CHAR_LIMIT)}
</div>
</div>
<div className={styles.detailsHeader}>Pool Details</div>
{amountOfPoolTokens.map((amount, index) => {
return (
<div key={index} className={styles.detailsRow}>
<div className={styles.detailsAttribute}>
Total{' '}
{tokens[index] === undefined
? 'loading...'
: tokens[index].symbol}
:
</div>
<div className={styles.detailsValue}>
{amount.substring(0, DISPLAY_CHAR_LIMIT)}
</div>
</div>
);
})}
<div className={styles.detailsRow}>
<div className={styles.detailsAttribute}>Total Share:</div>
<div className={styles.detailsValue}>
{totalShare.substring(0, DISPLAY_CHAR_LIMIT)}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
Here, we are implementing a component that displays detailed information about the user and the AMM pool.
Let’s take a look at the contents of Details.tsx.
type Props = {
token0: TokenType | undefined;
token1: TokenType | undefined;
amm: AmmType | undefined;
currentAccount: string | undefined;
updateDetailsFlag: number;
};
Argument specification:
token0 and token1 will each receive either the USDC or JOE object.
updateDetailsFlag acts as a trigger to update the information displayed in this component.
When this flag changes, the information will be refreshed, so it is included in the dependency array of the upcoming useEffect.
const [amountOfUserTokens, setAmountOfUserTokens] = useState<string[]>([]);
const [amountOfPoolTokens, setAmountOfPoolTokens] = useState<string[]>([]);
const [tokens, setTokens] = useState<TokenType[]>([]);
const [userShare, setUserShare] = useState("");
const [totalShare, setTotalShare] = useState("");
These are the state variables used to store the information handled by this component.
In this component, the token0 and token1 passed as arguments are stored in the tokens array for easier handling.
Other state variables that are arrays of type string correspond to the same order as tokens.
For example, if tokens = [token0, token1] is stored in that order, then the amountOfUserTokens array, which represents the amount of tokens owned by the user, will store information like this:
amountOfUserTokens = [amount of token0 owned by the user, amount of token1 owned by the user]
const getAmountOfUserTokens = useCallback(async () => {
if (!currentAccount) return;
try {
setAmountOfUserTokens([]);
for (let index = 0; index < tokens.length; index++) {
const amountInWei = await tokens[index].contract.balanceOf(
currentAccount
);
const amountInEther = ethers.utils.formatEther(amountInWei);
setAmountOfUserTokens((prevState) => [...prevState, amountInEther]);
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}, [currentAccount, tokens]);
The balanceOf function of each token contract is called to retrieve the amount of tokens owned by the user, and this value is stored in a state variable.
📓 About
useCallbackuseCallbackmemoizes a function.Normally, when a component (in this case,
Details) re-renders, its internal functions are recreated. Memoization prevents this recreation unless there is a change in the dependency array (here,[currentAccount, tokens]).In this case,
getAmountOfUserTokensis included in the dependency array of a subsequentuseEffect. Since we want to rungetAmountOfUserTokenswhen theDetailscomponent is rendered, we include the function in the dependency array. However, ifgetAmountOfUserTokenswere recreated on every re-render, it would cause theuseEffectto run again unnecessarily.References: https://ja.reactjs.org/docs/hooks-reference.html#usecallback https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57156582/should-i-wrap-all-functions-that-defined-in-component-in-usecallback
Other functions similarly retrieve specific information from the contract and store it in state variables.
📁 Container directory
Update the contents of Container.tsx as follows:
import { useState } from "react";
import { useContract } from "../../hooks/useContract";
import Details from "../Details/Details";
import styles from "./Container.module.css";
type Props = {
currentAccount: string | undefined;
};
export default function Container({ currentAccount }: Props) {
const [activeTab, setActiveTab] = useState("Swap");
const [updateDetailsFlag, setUpdateDetailsFlag] = useState(0);
const { usdc: token0, joe: token1, amm } = useContract(currentAccount);
const changeTab = (tab: string) => {
setActiveTab(tab);
};
const updateDetails = () => {
// The flag is toggled back and forth between 0 and 1.
setUpdateDetailsFlag((updateDetailsFlag + 1) % 2);
};
return (
<div className={styles.mainBody}>
<div className={styles.centerContent}>
<div className={styles.selectTab}>
<div
className={
styles.tabStyle +
" " +
(activeTab === "Swap" ? styles.activeTab : "")
}
onClick={() => changeTab("Swap")}
>
Swap
</div>
<div
className={
styles.tabStyle +
" " +
(activeTab === "Provide" ? styles.activeTab : "")
}
onClick={() => changeTab("Provide")}
>
Provide
</div>
<div
className={
styles.tabStyle +
" " +
(activeTab === "Withdraw" ? styles.activeTab : "")
}
onClick={() => changeTab("Withdraw")}
>
Withdraw
</div>
<div
className={
styles.tabStyle +
" " +
(activeTab === "Faucet" ? styles.activeTab : "")
}
onClick={() => changeTab("Faucet")}
>
Faucet
</div>
</div>
{activeTab === "Swap" && <div>swap</div>}
{activeTab === "Provide" && <div>provide</div>}
{activeTab === "Withdraw" && <div>withdraw</div>}
{activeTab === "Faucet" && <div>faucet</div>}
</div>
<Details
token0={token0}
token1={token1}
amm={amm}
currentAccount={currentAccount}
updateDetailsFlag={updateDetailsFlag}
/>
</div>
);
}
The main changes are as follows:
- Added state variables
const [updateDetailsFlag, setUpdateDetailsFlag] = useState(0); // A flag for updating user and pool details
const { usdc: token0, joe: token1, amm } = useContract(currentAccount); // Get the contract from useContract
- Implemented a function to toggle the flag Each time this function is executed, the flag switches between 0 and 1.
const updateDetails = () => {
The flag is toggled back and forth between 0 and 1.
setUpdateDetailsFlag((updateDetailsFlag + 1) % 2);
};
- Using the Details component
<Details
token0={token0}
token1={token1}
amm={amm}
currentAccount={currentAccount}
updateDetailsFlag={updateDetailsFlag}
/>
🖥️ Let’s check it on the screen
In the terminal, run the following command:
yarn client dev
Open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000.
If you see a screen like the one below, you’ve succeeded! On the right side of the screen, the user and pool details will be displayed.
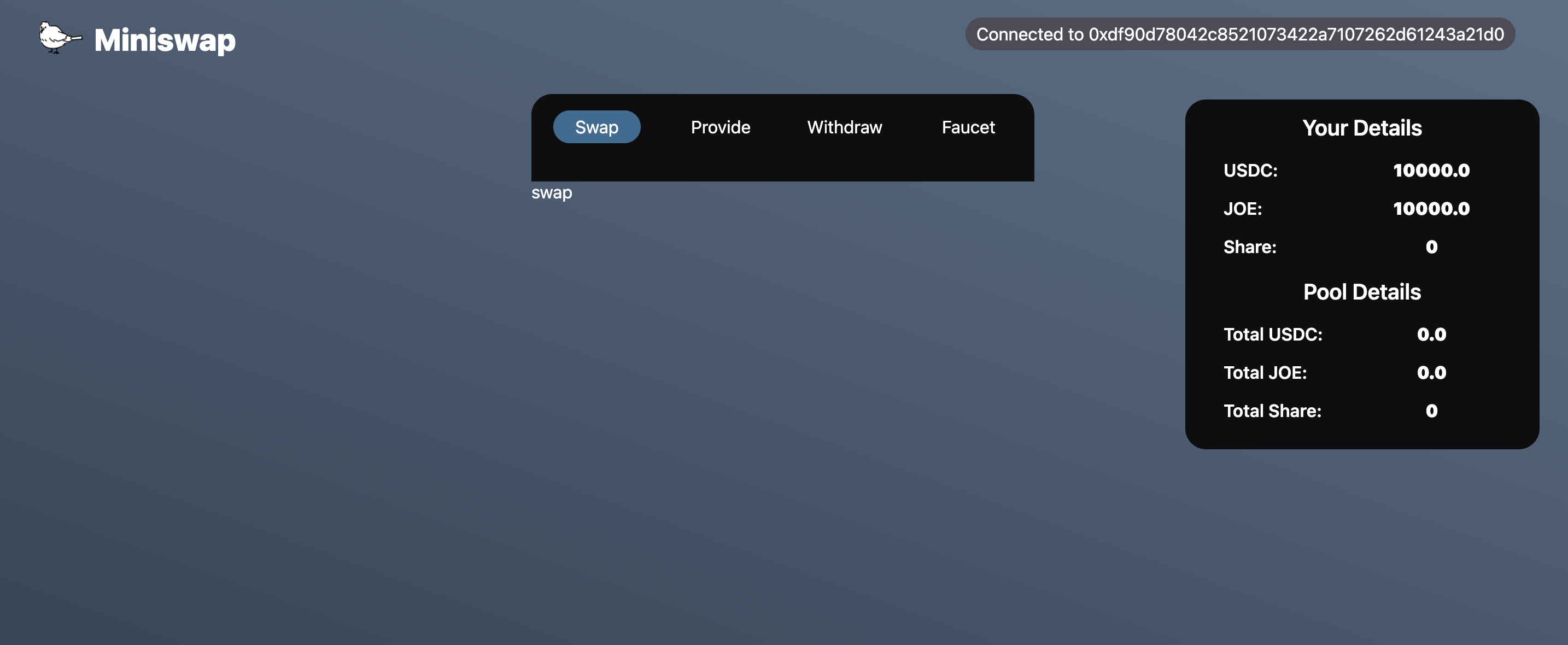
If you’re connected with the account you used to deploy the contract, the amount of each token you own should be 10000.
🌔 Reference Link
The completed repository for this project can be found here. If things don’t work as expected, feel free to check it for reference.
🙋♂️ Asking Questions
If you have any questions about what we’ve done so far, please ask in the #avalanche channel on Discord.
To make the support process smoother, include the following in your error report ✨
1. The section number and lesson number related to your question
2. What you were trying to do
3. Copy & paste the error message
4. Screenshot of the error screen
In the next lesson, we’ll complete the frontend 🎉