Understanding Swap
🐣 Let's Understand How Swap Works
In AMMs, the amount of tokens that can be swapped is determined according to an algorithm. Here, we use the same formula as Uniswap:
y is the amount of one token Y in the liquidity pool, and x is the amount of the other token X.
k is a constant. In other words, the product of the amounts of both tokens in the pool is always constant.
⚠️ In reality, k changes when considering fees during liquidity provisioning or swapping, but token prices are calculated based on the principle of:
When visualized, the formula draws the following curve:
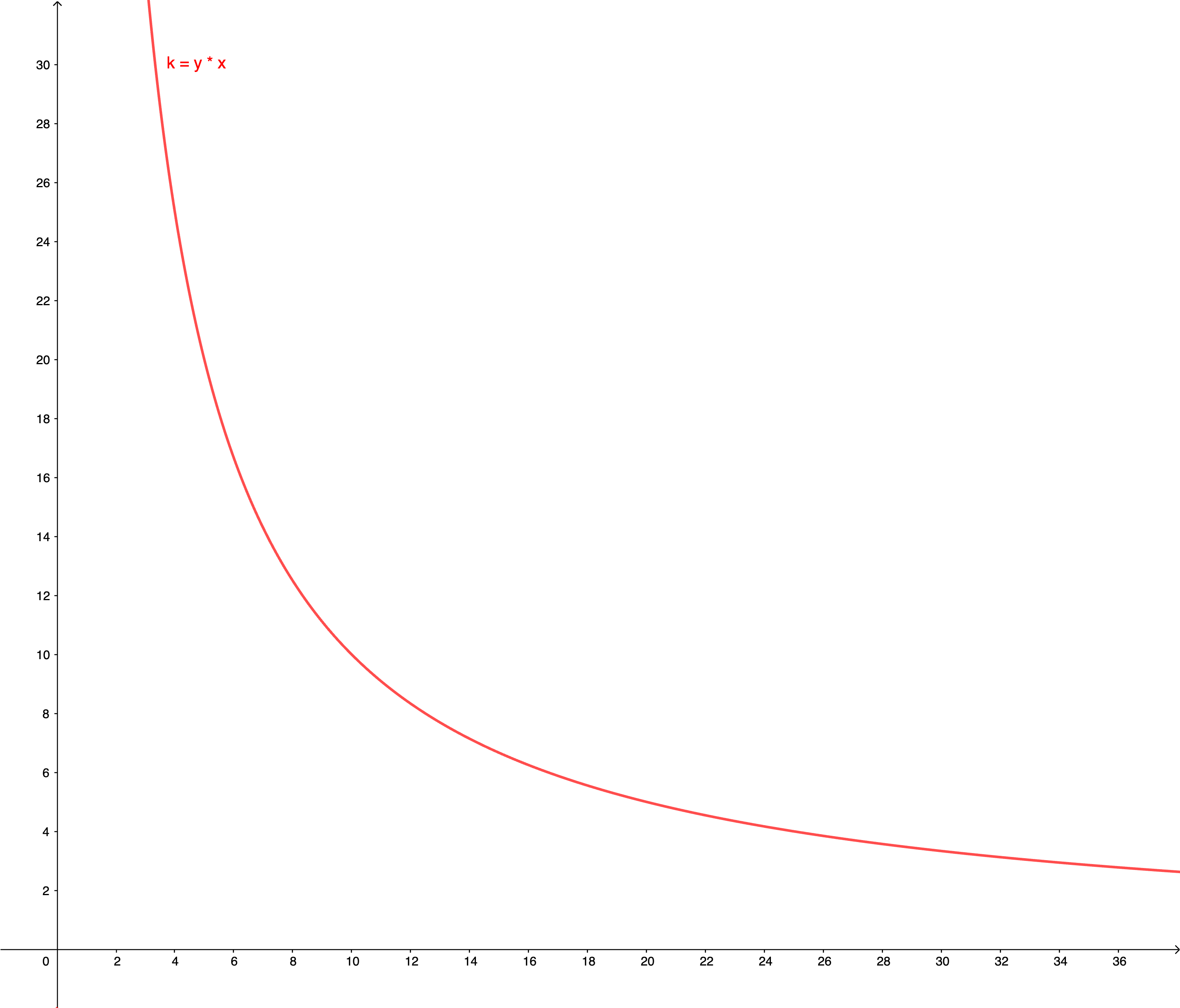
As the amount of x increases, the amount of y decreases, and vice versa.
So when swapping from token X to Y, X is sent from the user to the pool, increasing the amount of X in the pool. As a result, the amount of Y in the pool decreases. The swap is complete when the decreased amount of Y is sent to the user.
Let’s look at this process visually. When swapping from token X to Y, the change in token amounts in the pool can be represented as a movement from point A to point B in the figure below:
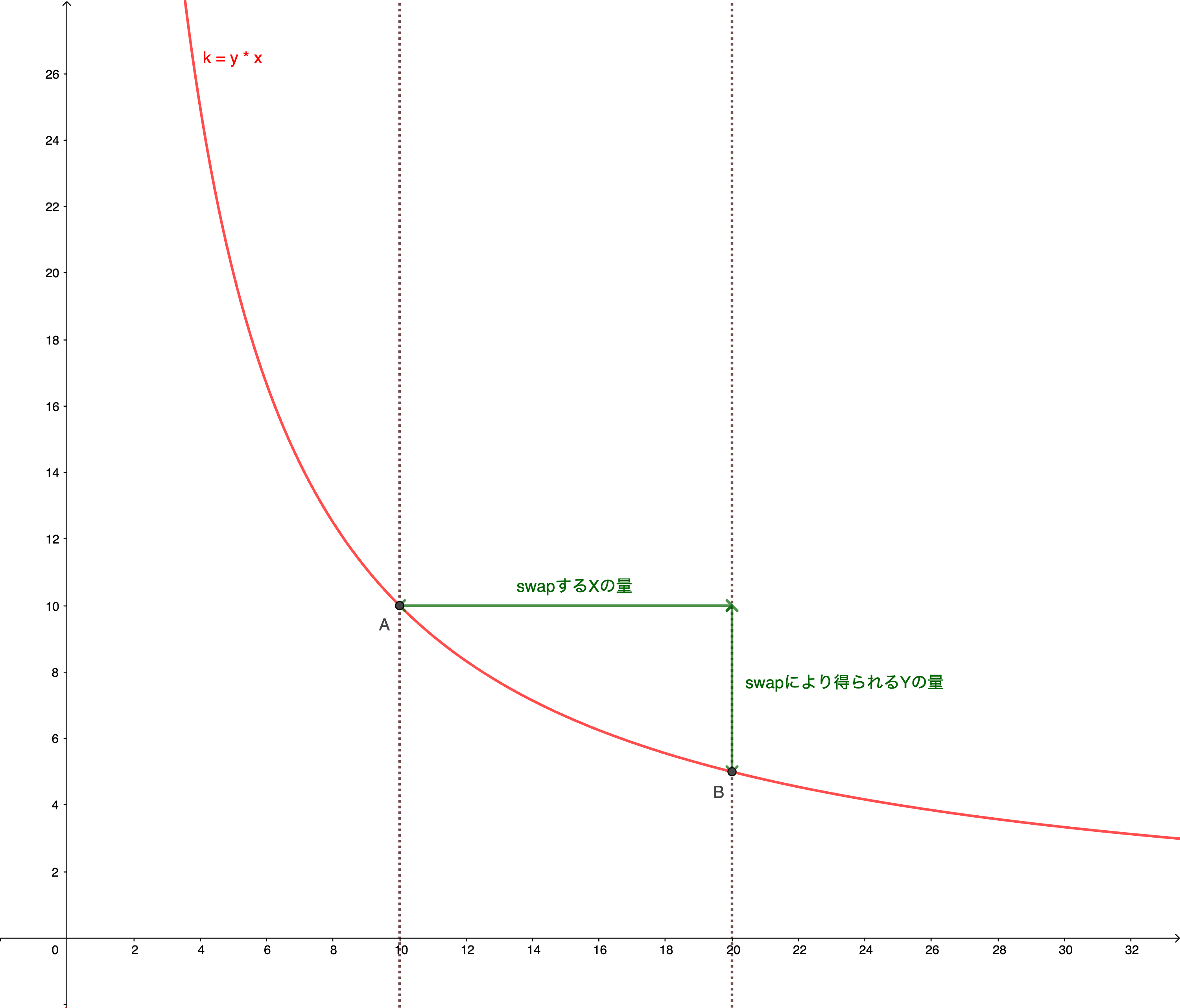
Conversely, a swap from token Y to X can be represented as:
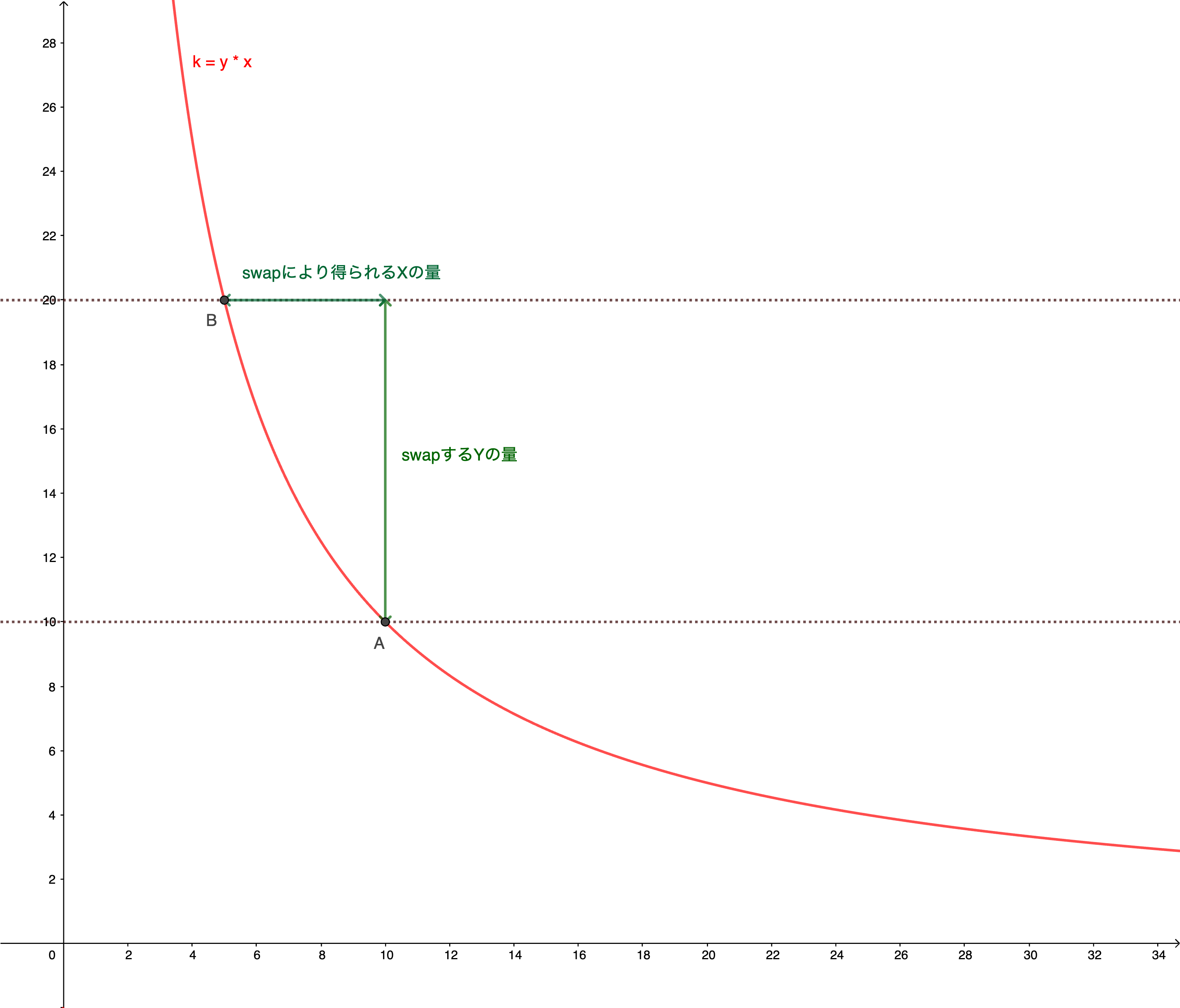
In this way, price determination inside the AMM is based on the core formula.
If swaps from X to Y continue and the amount of X in the pool increases, the amount of Y that can be received for the same amount of X decreases. The value of X drops, and the value of Y rises.
🏛️ Let’s Derive the Formula for the Amount of Tokens Obtained in a Swap
Now we consider how the AMM contract should calculate the amount of tokens to send to the user in response to a swap request.
If it’s hard to follow, feel free to continue to the implementation first and revisit this lesson later.
You can also ask in Discord’s #avalanche channel.
If you find any mistakes, feel free to submit a pull request here.
Let’s derive the formula for the following situation:
Suppose the pool contains x of token X and y of token Y.
A user provides token X and receives token Y(a swap from X to Y).
Let x' be the amount of token X added, and y' be the amount of token Y received.
🦕 Situation 1: Deriving y' from x'

We derive a method to calculate the amount y' to be received from a known amount x' added to the pool.
The base formula is as follows, where K is constant:
Even after changes in x' and y', the product of X and Y remaining in the pool must be constant:
The left side of the equation represents point A in the figure above, and the right side represents point B. Now, we solve the equation for y':
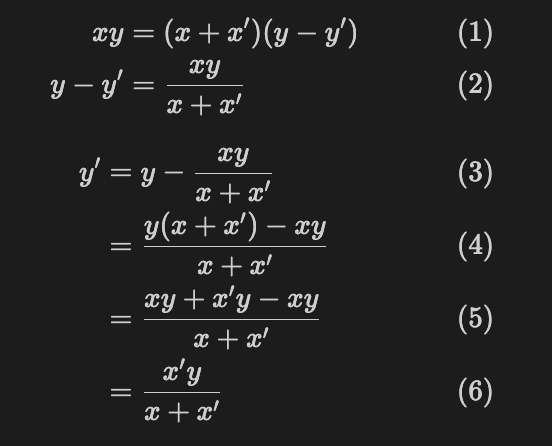
A simple formula has been derived. We can use this to calculate y'.
🐬 Situation 2: Deriving x' from y'
The figure is the same as in Situation 1:

Now, we reverse the problem: y' is specified in advance, and we want to know how much x' needs to be added to the pool.
The calculation is nearly the same as before, but this time we solve for x':
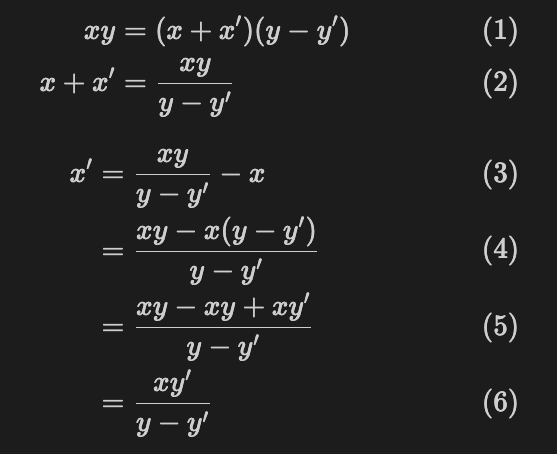
From the above, we understand that:
- To determine the amount of tokens to be received based on the input amount, use the formula from Situation 1
- To determine the required input amount to receive a specified amount, use the formula from Situation 2
🙋♂️ Ask Questions
If you have any questions so far, please ask in Discord’s #avalanche channel.
To make the help process smoother, please include the following in your error report ✨
1. The section and lesson number related to the question
2. What you were trying to do
3. Copy & paste of the error message
4. Screenshot of the error screen
Now that you’ve understood swap, let’s deepen our understanding of swap fees in the next lesson 🎉